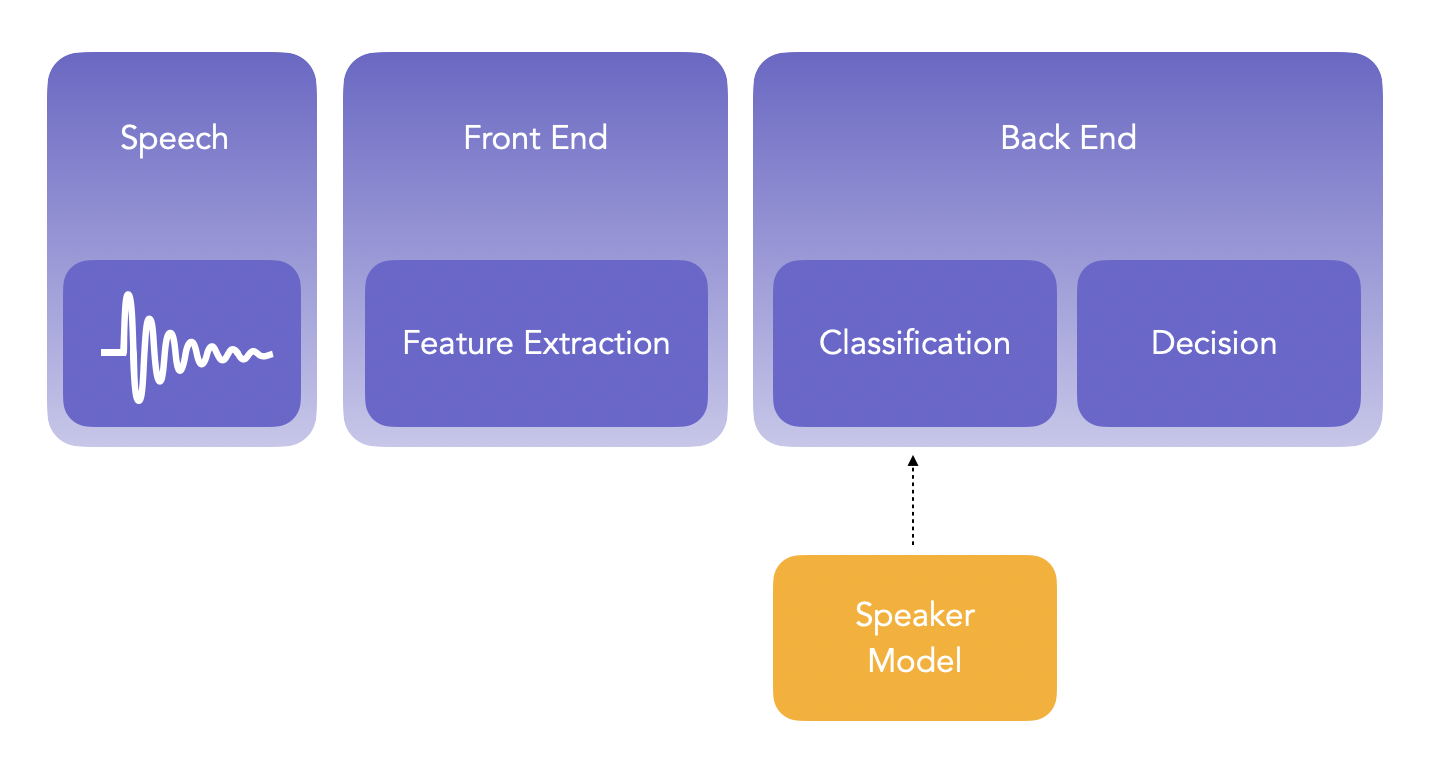
Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis (PLDA)[http://people.irisa.fr/Guillaume.Gravier/ADM/articles2018/Probabilistic_Linear_Discriminant_Analysis.pdf] brought a major contribution to the field of both computer vision and speech processing, especially for the task of speaker identification and verification.
PLDA relies on Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), which is a linear dimensionality reduction method. While PCA identifies the linear subspace in which most of the data’s energy is concentrated, LDA identifies the subspace in which the data between different classes is most spread out, relative to the spread within each class. Hence, LDA can be used for classification.
I wrote a quick illustrated article on LDA if you want to check it.
Among the limitations of LDA, one can cite:
- the fact that LDA cannot predict unseen classes (as we do in speaker verification and face recognition)
- the fact that LDA typically relies on a PCA step, and we don’t know which dominant projection directions identified by LDA is contributing to the object or voice recognition task
TO CONTINUE