Easy Question Answering with AllenNLP
AllenNLP is an Apache 2.0 NLP research library, built on PyTorch, for developing state-of-the-art deep learning models on a wide variety of linguistic tasks. AllenNLP is built and maintained by the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence, in close collaboration with researchers at the University of Washington and elsewhere.
What is Question Answering?
Question Answering (QA), or Machine Comprehension (MC) aims to answer a query about a given context by modeling the interactions between both context and queries. Typical approaches in QA rely on attention mechanismes, in order to focus on a small part of the text and summarize it with a fixed-size vector.
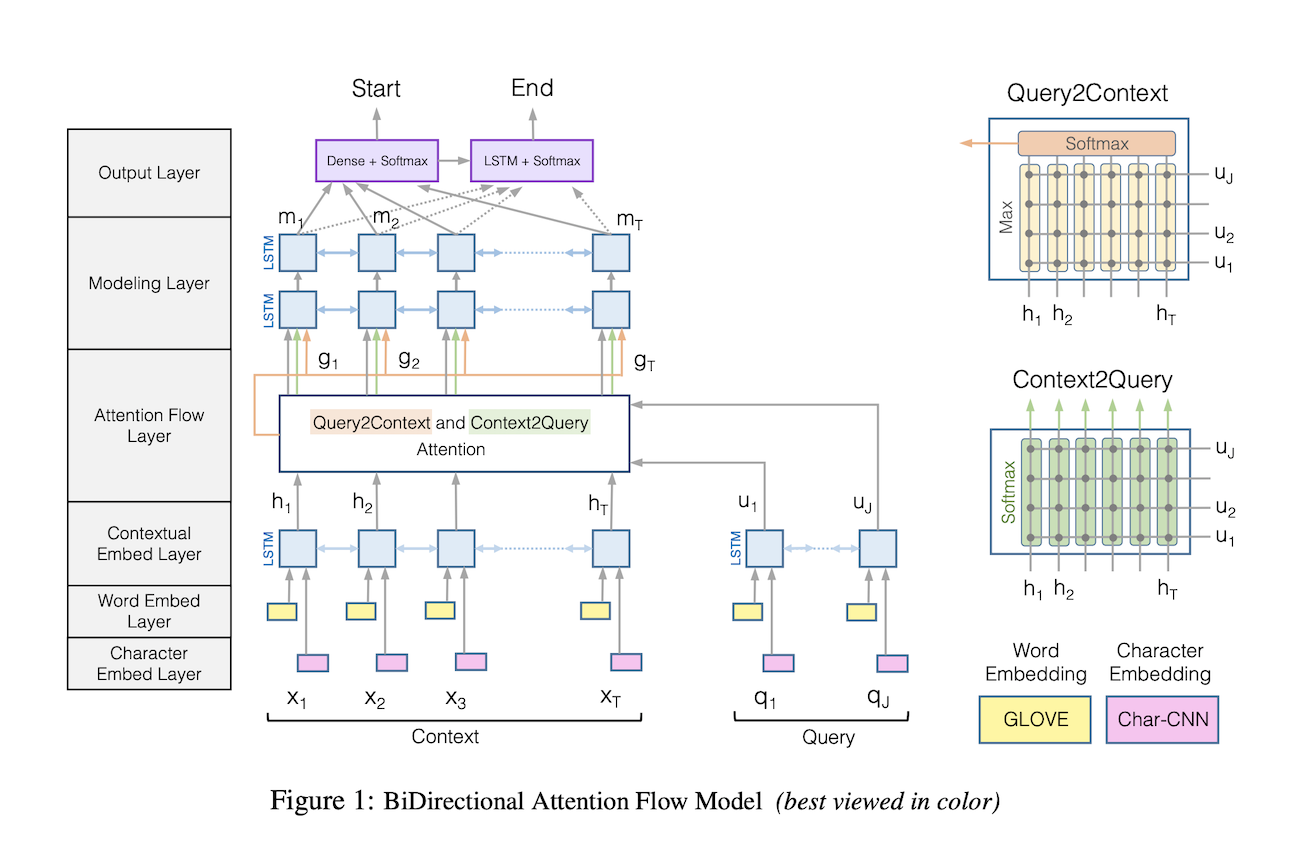
AllenNLP implements a pre-trained Bi-Directional Attention Flow (BIDAF). This network is a multi-stage hierarchical process that represents the context at different levels of granularity and uses bidirectional attention flow mechanism to obtain a query-aware context representation without early summarization. This approach was published in 2017 by the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence in this paper.
According to the original paper, the steps of the BIDAF are the following:
- Character Embedding Layer maps each word to a vector space using character-level CNNs.
- Word Embedding Layer maps each word to a vector space using a pre-trained word embedding model.
- Contextual Embedding Layer utilizes contextual cues from surrounding words to refine the embedding of the words. These first three layers are applied to both the query and context.
- Attention Flow Layer couples the query and context vectors and produces a set of queryaware feature vectors for each word in the context.
- Modeling Layer employs a Recurrent Neural Network to scan the context.
- Output Layer provides an answer to the query.
Using AllenNLP’s library
To install AllenNLP, simply run :
pip install allennlp
If you have SpaCy installed and encounter some issues with your current SpaCy version, I encourage you to switch to version 2.1.8 of SpaCy and downgrade the en_core_news package to version 2.1.0. This worked out for me. We’ll deploy this pre-trained QA algorithm on a Streamlit web application. To do so, import the following packages:
from allennlp import pretrained
import streamlit as st
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Then, start to build the application:
st.title("Question Answering")
# Avoids loading the model each time in streamlit
# Loads the model
model = st.cache(
pretrained.bidirectional_attention_flow_seo_2017,
allow_output_mutation=True
)()
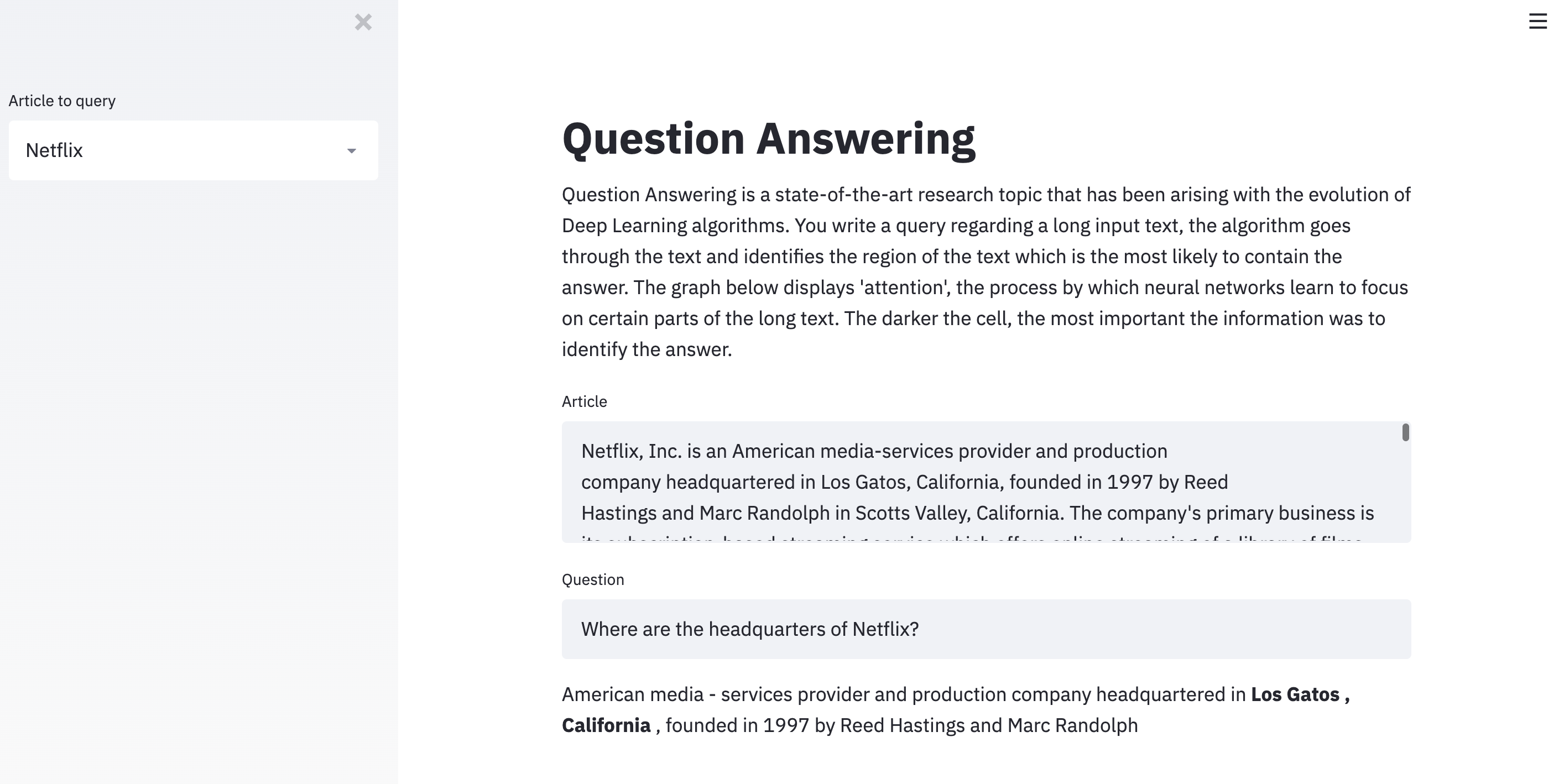
Once the pre-trained model has been loaded, we can run it on the Wikipedia article of Netflix:
passage = st.text_area("Article", """Netflix, Inc. is an American media-services provider and production company headquartered in Los Gatos, California, founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California. The company's primary business is its subscription-based streaming service which offers online streaming of a library of films and television programs, including those produced in-house. As of April 2019, Netflix had over 148 million paid subscriptions worldwide, including 60 million in the United States, and over 154 million subscriptions total including free trials. It is available worldwide except in mainland China (due to local restrictions), Syria, North Korea, and Crimea (due to US sanctions). The company also has offices in the Netherlands, Brazil, India, Japan, and South Korea. Netflix is a member of the Motion Picture Association (MPA). Netflix's initial business model included DVD sales and rental by mail, but Hastings abandoned the sales about a year after the company's founding to focus on the initial DVD rental business. Netflix expanded its business in 2010 with the introduction of streaming media while retaining the DVD and Blu-ray rental business. The company expanded internationally in 2010 with streaming available in Canada, followed by Latin America and the Caribbean. Netflix entered the content-production industry in 2012, debuting its first series Lilyhammer. Since 2012, Netflix has taken more of an active role as producer and distributor for both film and television series, and to that end, it offers a variety of "Netflix Original" content through its online library. By January 2016, Netflix services operated in more than 190 countries. Netflix released an estimated 126 original series and films in 2016, more than any other network or cable channel. Their efforts to produce new content, secure the rights for additional content, and diversify through 190 countries have resulted in the company racking up billions in debt: $21.9 billion as of September 2017, up from $16.8 billion from the previous year. $6.5 billion of this is long-term debt, while the remaining is in long-term obligations. In October 2018, Netflix announced it would raise another $2 billion in debt to help fund new content.""")
We must then define a question to ask:
question = st.text_input("Question", "Where are the headquarters of Netflix?")
We compute the result easily through this function:
result = model.predict(question, passage)
From the result, we want the “best_span”, “question_tokens”, and “passage_tokens” which contain respectively the position of the answer, a tokenized version of the question and a tokenized version of the article/passage.
start, end = result["best_span"]
question_tokens = result["question_tokens"]
passage_tokens = result["passage_tokens"]
In order to display the result, we will only pick the 10 words before and the 10 words after the answer. We also display in bold the exact words which contain the answer:
mds = [f"**{token}**" if start <= i <= end else token if start - 10 <= i <= end + 10 else "" for i, token in enumerate(passage_tokens)]
st.markdown(" ".join(mds))
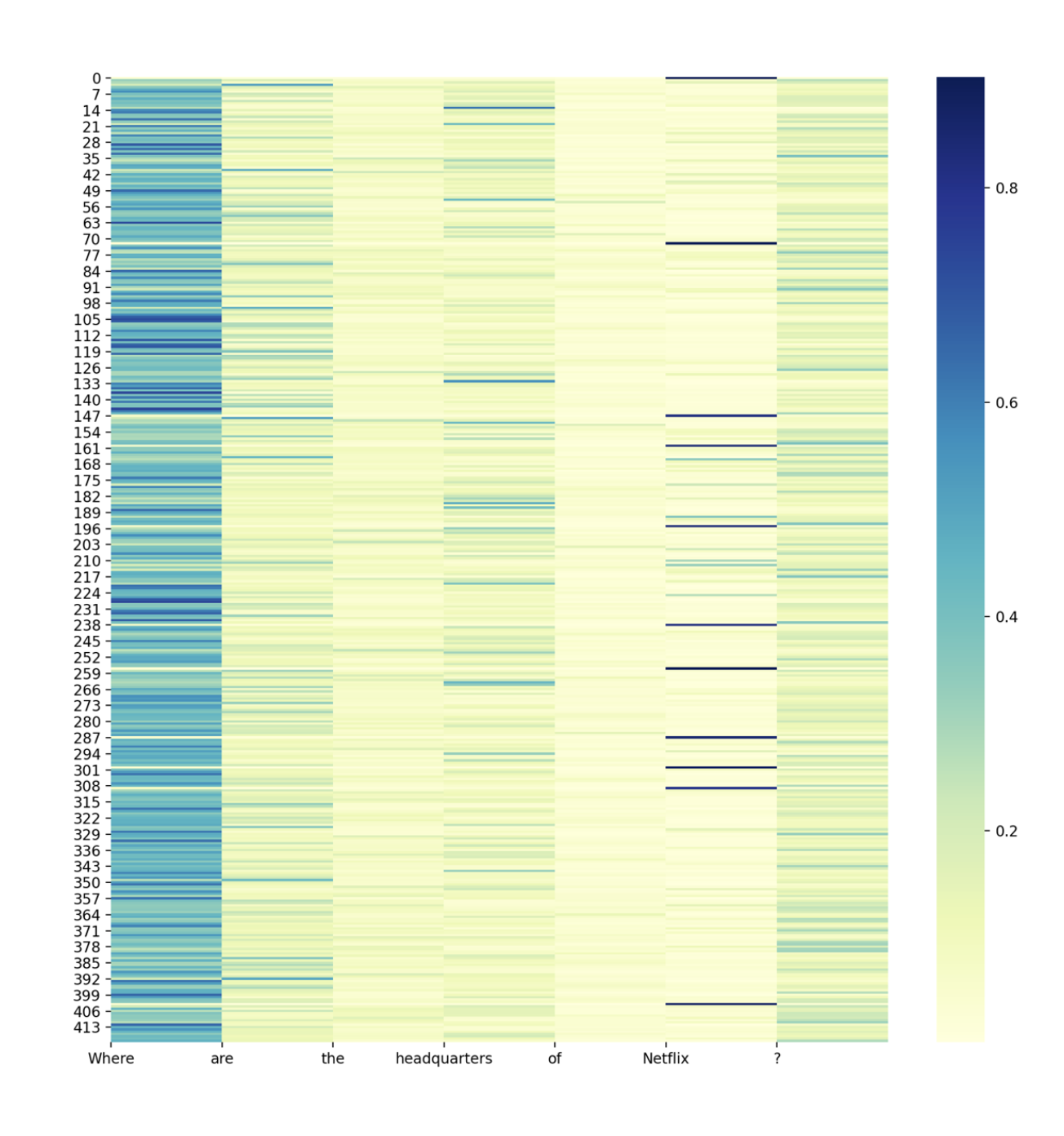
At that moment, the web application works well but the explainability remains limited. In order to imporve that, we can plot the attention layers. The X-axis represents the question, and the Y-axis represents the input text. The darker the column, the most important the attention is in this area. We notice that words such as “When” or “Where” play a big word in the attention layers, since they expect a date or a place in return.
attention = result["passage_question_attention"]
plt.figure(figsize=(12,12))
sns.heatmap(attention, cmap="YlGnBu")
plt.autoscale(enable=True, axis='x')
plt.xticks(np.arange(len(question_tokens)), labels=question_tokens)
st.pyplot()
Conclusion : I hope that this introduction was useful. I simply wanted to demonstrate how easy it can be to create a small QA web service.
