The Bayes Classifier is a binary classification algorithm. It is often introduced as one of the first algorithms to master in the field of machine learning. Bayes classifier is called Generative since it is trained to learn the distribution of both marginal classes, instead of the decision frontier itself.
In each article, I try to summarize the key idea of each algorithm in just a few lines.
Key ideas
- Generative Model that tries to estimate \(P (X = x \mid Y = 1)\) and \(P (X = x \mid Y = -1)\)
- Used for binary classification
- Relies on knowing \(\eta (x) = P (Y = 1 \mid X = x)\) and can therefore never be acheived
- Similar to knowing the decision frontier itself
Bayes Classifier
In binary classification, we’ll try to predict labels : \(Y\) is either \(1\) or \(-1\) . The datas we use is a matrix \(X\) of observations with \(d\) features.
Let \(\eta (x) = P (Y = 1 \mid X = x)\) be the prior probability.
Our aim is to define a classification function \(g\), i.e \(g(X) \in (-1,1)\) such that : \(g(x) = 1 if \eta(x) ≥ \frac {1} {2}\) and \(g(x) = -1 if \eta(x) < \frac {1} {2}\).
These two constraints can be combined in a single constraint :
\[g(x) = 2 I(\eta(x) ≥ \frac {1} {2}) -1\]\(g(x)\) is called the Bayes Classifier.
The Bayes classifier can never be reached since it would imply knowing the decision frontier before the classification process. Bayes classifier is the optimal classifier!
Theory behind Bayes
Bayes classifier uses the so-called Bayes Rule whose fundamental result states that for two given event \(Y\) and \(X\) :
\[ℙ(Y \mid X) = \frac {ℙ(X \mid Y)P(Y)} {P(X)}\]Bayes classifier is a Generative model in the sense that we estimate the decision frontier using the marginal distributions \(ℙ(X \mid Y)\).
Graphically, the distributions of \(ℙ(X \mid Y = 1)\) and \(ℙ(X \mid Y = -1)\) are represented by the two ellipses, and the decision boundary is the black line.
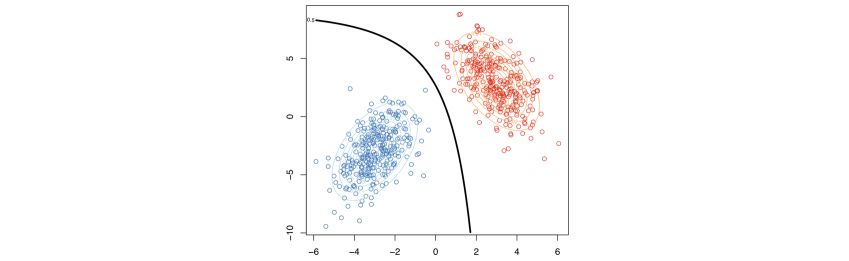
Plug-in principle
In most of the other classifiers we’ll cover, we are going to use the plug-in principle. The idea is to estimate \(\eta (x)\) the desicion boundary by \(\hat{\eta} (x)\), and then plug-in this estimator into the classifier, such that :
\[g(x) = 2 I(\hat{\eta}(x) ≥ \frac {1} {2}) -1\]Conclusion : In the next articles, we’ll cover the most common classifiers in supervised learning theory. Don’t hesitate to drop a comment if you have any question.
