In this lab, we suppose that we have an existing on-premise architecture for housing rental recommendation. Our aim will be to migrate this infrastructure to GCP. Machine Learning is done using PySpark SparkML library.
Create Cloud SQL instances
On the GCP Console, from the Storage tab, click on “SQL”, and create an instance.
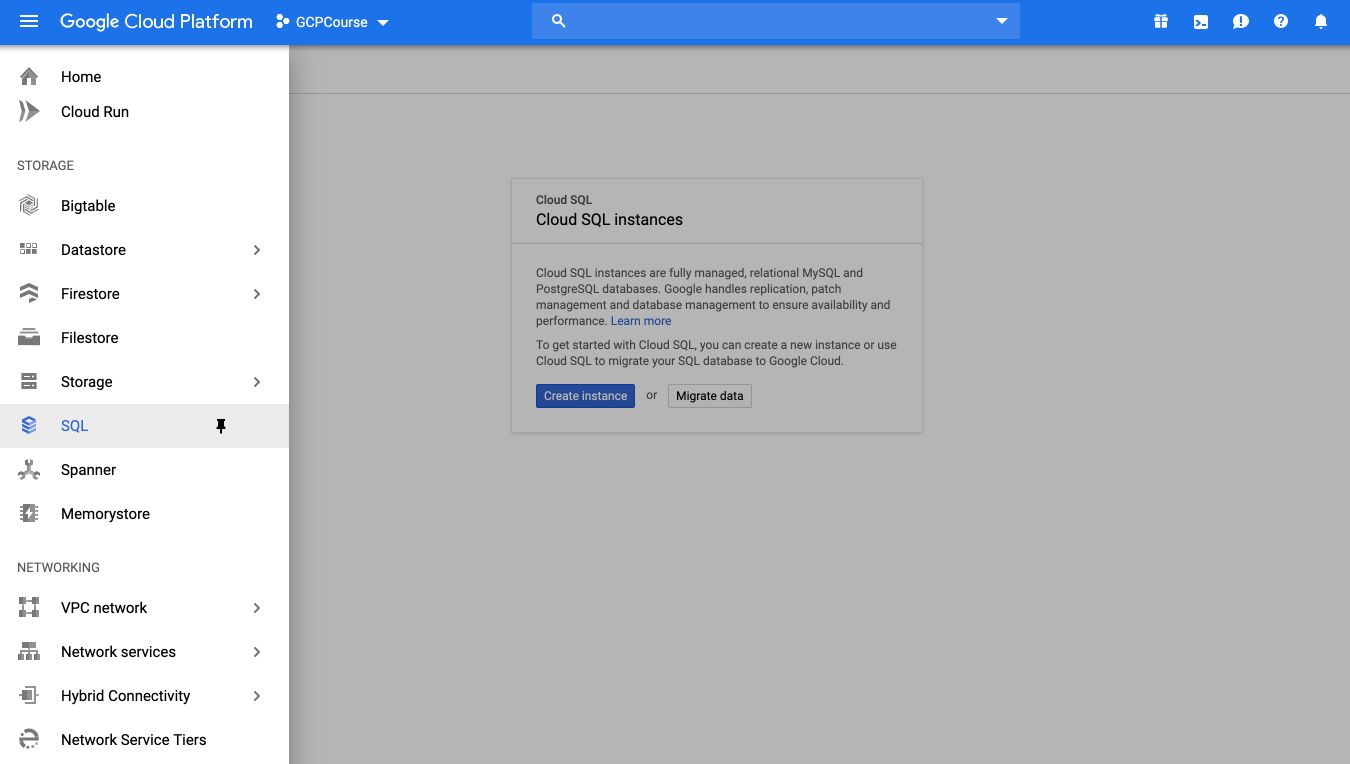
Select the MySQL instance.
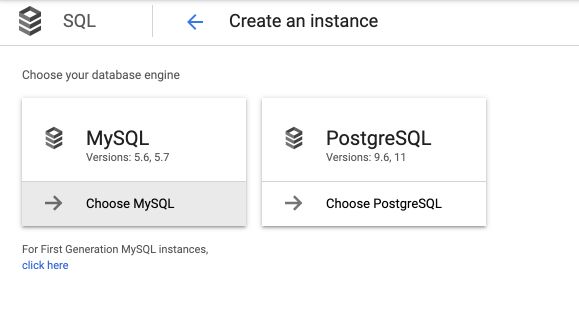
Set the instance name to rentals and define a password (make sure to remember it) :
Allocate 2 vCPUs to your Master and Nodes.
The instance will then start :

You’ll have to wait a few minutes in order for the instance to be ready. Once ready (after 5 minutes usually), click on the name of the instance to access instance details. On the main page, you’ll notice a button to connect to the instance using Cloud Shell :
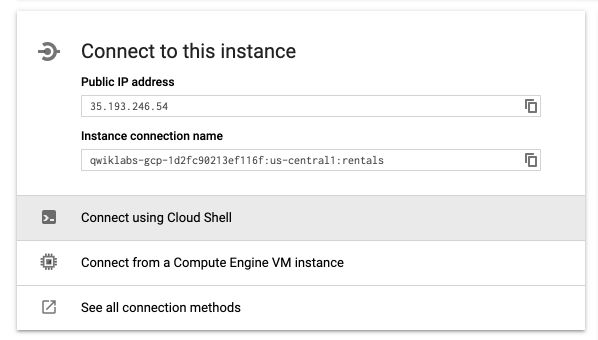
A Cloud Shell will start. Type Enter and wait for the whitelisting of your IP address.
google4448450_student@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-1d2fc90213ef116f)$ gcloud sql connect rentals --user=root --quiet
Whitelisting your IP for incoming connection for 5 minutes...⠹
When required, type your password. Your shell should look like this :
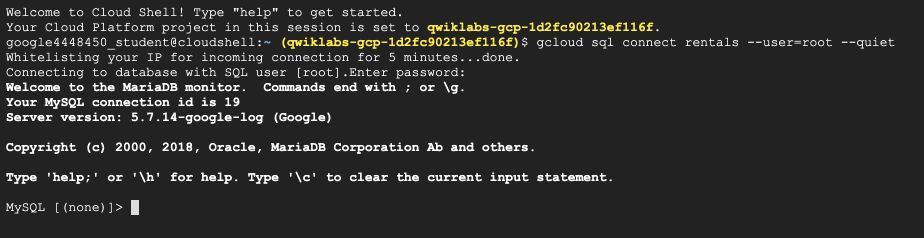
A SQL shell is now ready. You can type SQL queries. Start for example with :
SHOW DATABASES;
Create tables
It should the structure of the existing database. We will then create 3 tables :
- a Recommendation table that attache recommendation to a user I
- an Accommodation table that describes the accommodation
- a Rating table that describes the rating of each accommodation
To create the tables, run the following query :
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS recommendation_spark;
USE recommendation_spark;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Recommendation;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Rating;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Accommodation;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Accommodation
(
id varchar(255),
title varchar(255),
location varchar(255),
price int,
rooms int,
rating float,
type varchar(255),
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Rating
(
userId varchar(255),
accoId varchar(255),
rating int,
PRIMARY KEY(accoId, userId),
FOREIGN KEY (accoId)
REFERENCES Accommodation(id)
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Recommendation
(
userId varchar(255),
accoId varchar(255),
prediction float,
PRIMARY KEY(userId, accoId),
FOREIGN KEY (accoId)
REFERENCES Accommodation(id)
);
SHOW DATABASES;
We will use the recommendation_spark table :
MySQL [recommendation_spark]> USE recommendation_spark;
Database changed
MySQL [recommendation_spark]> SHOW TABLES;
+--------------------------------+
| Tables_in_recommendation_spark |
+--------------------------------+
| Accommodation |
| Rating |
| Recommendation |
+--------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.11 sec)
MySQL [recommendation_spark]>
Store data in Google Cloud Storage
Alright, how do we import data in those tables then? There are 2 options, either through the UI or through the command lines. Here, we will use the command lines. Open a new tab in the Shell and type the following command :
echo "Creating bucket: gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID"
gsutil mb gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID
echo "Copying data to our storage from public dataset"
gsutil cp gs://cloud-training/bdml/v2.0/data/accommodation.csv gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID
gsutil cp gs://cloud-training/bdml/v2.0/data/rating.csv gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID
echo "Show the files in our bucket"
gsutil ls gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID
echo "View some sample data"
gsutil cat gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID/accommodation.csv
These lines (using gsuitl) load the accommodation and rating CSV files. The last line (gsutil cat) displays the content a preview of the accommodation table.
gsutil cat gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID/accommodation.csv
1,Comfy Quiet Chalet,Vancouver,50,3,3.1,cottage
2,Cozy Calm Hut,London,65,2,4.1,cottage
3,Agreable Calm Place,London,65,4,4.8,house
4,Colossal Quiet Chateau,Paris,3400,16,2.7,castle
5,Homy Quiet Shack,Paris,50,1,1.1,cottage
Move data from Cloud Storage to Cloud SQL
At that point, the data is in Google Cloud Storage. Our tables are however in Cloud SQL. We need to move the files in the SQL tables. From the SQL instance details page, click on “Import” :
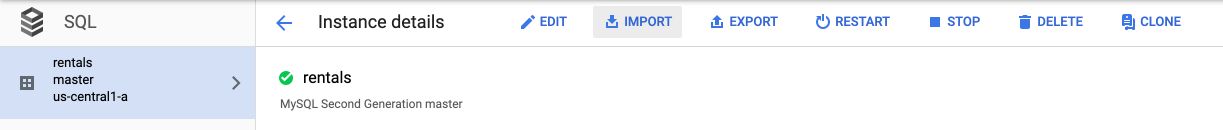
Apply the following procedure for both accomodation.csv and rating.csv :
- browse and select the file
- make sure the format is in CSV
- select
recommendation_sparkas the database - give it the names Accomoddation or Rating respectively (or anything else if you changed the names of the tables when you created them)

Explore data from Cloud SQL
To display the content of the rating tables, go back to the SQL instance name, and connect to the instance using Cloud shell. Wait a bit and type your password. From the Shell, start exploring the data by running SQL queries :
SELECT * FROM Rating
LIMIT 15;
We can build SQL queries to see how many ratings we have overall :
SELECT COUNT(*) AS num_ratings
FROM Rating;
Or find the user that wrote the most ratings :
SELECT userId,
COUNT(rating) AS num_ratings
FROM Rating
GROUP BY userId
ORDER BY num_ratings DESC;
We won’t need the SQL shell anymore, you can safely exit :
exit
Launch Dataproc
As discussed in a previous article, we need to allow Cloud Dataproc to connect with Cloud SQL, since the computation and the storage are split.
You need to create a Cloud Dataproc cluster as we did in the previous lab. Name the cluster rentals, and leave all settings to their default value.
We now need to allow Dataproc to access this specific SQL Cluster. You might need to change the CLUSTER, CLOUDSQL, ZONE or NWORKERS variables if you changed something previously. On the shell that is remaining (not the SQL one), execute the following command :
echo "Authorizing Cloud Dataproc to connect with Cloud SQL"
CLUSTER=rentals
CLOUDSQL=rentals
ZONE=us-central1-a
NWORKERS=2
machines="$CLUSTER-m"
for w in `seq 0 $(($NWORKERS - 1))`; do
machines="$machines $CLUSTER-w-$w"
done
echo "Machines to authorize: $machines in $ZONE ... finding their IP addresses"
ips=""
for machine in $machines; do
IP_ADDRESS=$(gcloud compute instances describe $machine --zone=$ZONE --format='value(networkInterfaces.accessConfigs[].natIP)' | sed "s/\[u'//g" | sed "s/'\]//g" )/32
echo "IP address of $machine is $IP_ADDRESS"
if [ -z $ips ]; then
ips=$IP_ADDRESS
else
ips="$ips,$IP_ADDRESS"
fi
done
echo "Authorizing [$ips] to access cloudsql=$CLOUDSQL"
gcloud sql instances patch $CLOUDSQL --authorized-networks $ips
Load ML models
The ML models are already built in this exercise. We need to load the models (as if they were already built by the Data Science teams). The script is written in PySpark.
gsutil cp gs://cloud-training/bdml/v2.0/model/train_and_apply.py train_and_apply.py
We then need to edit the file :
cloudshell edit train_and_apply.py
Replace your Cloud SQL IP (most likely your project name), and your password :

You can save the file and quit the editor.
Then, copy this file to your Cloud Storage bucket using this Cloud Shell command:
gsutil cp train_and_apply.py gs://$DEVSHELL_PROJECT_ID
Run Jobs on DataProc
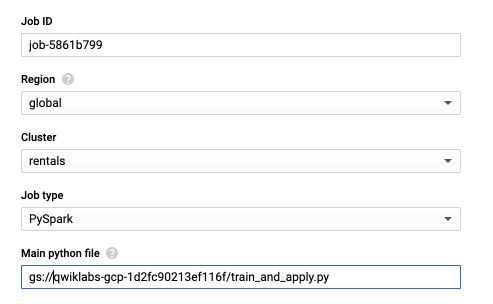
We can now run our ML jobs on Dataproc. On the DataProc Job tab, click on “Submit Job” :
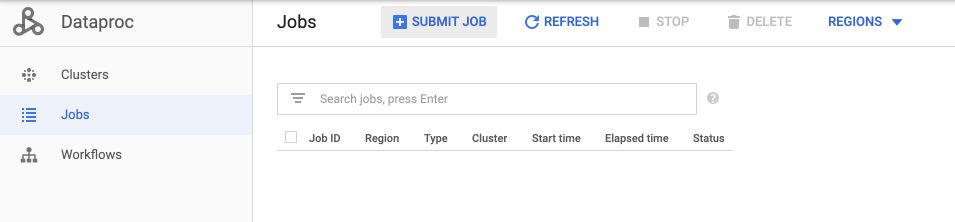
Change the name of the cluster to rentals, and the Job type to PySpark. For the main Python file, it should have the following format :
gs://<bucket-name>/train_and_apply.py
Where you can replace your bucket name. In my example :
The job should take around 5 minutes to run.
Explore results
If you still have your SQL Shell, use it again (launch it as previously).
We will use the recommenation_spark table.
USE recommendation_spark;
SELECT COUNT(*) AS count FROM Recommendation;
For a given user, we retrieve the recommendations in the following way :
SELECT
r.userid,
r.accoid,
r.prediction,
a.title,
a.location,
a.price,
a.rooms,
a.rating,
a.type
FROM Recommendation as r
JOIN Accommodation as a
ON r.accoid = a.id
WHERE r.userid = 10;
+--------+--------+------------+-------------------------+--------------+-------+-------+--------+---------+
| userid | accoid | prediction | title | location | price | rooms | rating | type |
+--------+--------+------------+-------------------------+--------------+-------+-------+--------+---------+
| 10 | 21 | 1.5929456 | Big Peaceful Cabin | Seattle | 80 | 2 | 4.9 | cottage |
| 10 | 31 | 1.4377488 | Colossal Private Castle | Buenos Aires | 1400 | 15 | 3.3 | castle |
| 10 | 41 | 1.3913738 | Big Calm Manor | Seattle | 800 | 11 | 2.7 | mansion |
| 10 | 7 | 1.32196 | Vast Peaceful Fortress | Seattle | 3200 | 24 | 1.9 | castle |
| 10 | 2 | 1.3101096 | Cozy Calm Hut | London | 65 | 2 | 4.1 | cottage |
+--------+--------+------------+-------------------------+--------------+-------+-------+--------+---------+
