Big Data tools are great, but if you have to learn a new language every time you use a new tool, this slows down the development of such tools. For this reason, it is possible to submit Python scripts to Hadoop using a Map-Reduce framework. Let’s consider the WordCount example.
Any job in Hadoop must have two phases:
- Mapper
- and Reducer.
Hadoop Streaming
Hadoop Streaming is the canonical way of supplying any executable to Hadoop as a mapper or reducer, including standard Unix tools or Python scripts. The executable must read from stdin and write to stdout using agreed-upon semantics.
- First, create a mapper that attaches the value 1 to every single word in the document. Copy-paste this code into a mapper.py file.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
words = line.split()
for word in words:
print('%s\t%s' % (word, 1))
- Then, create the reducer. Try to understand then copy-paste this code into a reducer.py file.
#!/usr/bin/env python
from operator import itemgetter
import sys
current_word = None
current_count = 0
word = None
for line in sys.stdin:
line = line.strip()
word, count = line.split('\t', 1)
try:
count = int(count)
except ValueError:
continue
if current_word == word:
current_count += count
else:
if current_word:
print('%s\t%s' % (current_word, current_count))
current_count = count
current_word = word
if current_word == word:
print('%s\t%s' % (current_word, current_count))
Save the two files in the VM, at the root : [raj_ops@sandbox-hdp ~], using scp :
-
scp -P 2222 Desktop/Hadoop/mapper.py raj_ops@localhost:mapper.py -
scp -P 2222 Desktop/Hadoop/reducer.py raj_ops@localhost:reducer.py
We can try our program locally using the following command :
echo "foo foo quux labs foo bar quux" | python mapper.py | sort -k1,1 | python reducer.py
If it returns :
bar 1foo 3labs 1quux 2
Then we can move on to the next step.
We are ready to launch the job for the terminal of the VM (after SSH connexion):
hadoop jar /usr/hdp/current/hadoop-mapreduce-client/hadoop-streaming.jar -input TP/input -output TP/output_python -mapper ./mapper.py -reducer ./reducer.py -file ./mapper.py -file ./reducer.py
Note that the files mapper.py and reducer.py must be specified twice on the command line: the first time points Hadoop at the executables, while the second time tells Hadoop to distribute the executables around to all the nodes in the cluster.
We run the Java class hadoop-streaming but using our Python files mapper.py and reduce.py as the MapReduce process.
You’ll see something like this :
19/05/19 20:20:36 INFO mapreduce.Job: Job job_1558288385722_0012 running in uber mode : false
19/05/19 20:20:36 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 0% reduce 0%
19/05/19 20:20:53 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 100% reduce 0%
19/05/19 20:21:09 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 100% reduce 84%
19/05/19 20:21:12 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 100% reduce 98%
19/05/19 20:21:13 INFO mapreduce.Job: map 100% reduce 100%
First, we cover the Map, then the reduce. The output is created in the TP/output_python of HDFS.
You can read the output and you’ll see :
" 278
"#Muscular 1
"'Come 1
"'Dieu 1
"'Dio 1
"'From 1
"'Grant 1
"'I 4
"'No 1
"'Now 1
"'Russia 1
...
mrJob
mrjob is an open-source Python framework that wraps Hadoop Streaming and is actively developed by Yelp. Since Yelp operates entirely inside Amazon Web Services, mrjob’s integration with EMR is incredibly smooth and easy (using the boto package). Check this link for more information.
from mrjob.job import MRJob
import re
WORD_RE = re.compile(r"[\w']+")
class MRWordFreqCount(MRJob):
def mapper(self, _, line):
for word in WORD_RE.findall(line):
yield (word.lower(), 1)
def combiner(self, word, counts):
yield (word, sum(counts))
def reducer(self, word, counts):
yield (word, sum(counts))
dumbo
dumbo is another Python framework that wraps Hadoop Streaming. It seems to enjoy relatively broad usage but is not developed as actively as mrjob at this point. It is one of the earlier Python Hadoop APIs and is very mature. However, its documentation is lacking, which makes it a bit harder to use.
hadoopy
hadoopy is another Streaming wrapper that is compatible with dumbo. Similarly, it focuses on typed bytes serialization of data and directly writes typed bytes to HDFS.
Summary
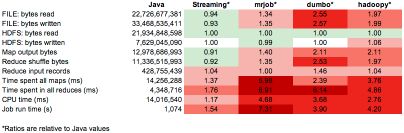
Hadoop Streaming outperforms other approaches, so simply remember that this approach works well.
Conclusion: I hope this tutorial was clear and helpful. I’d be happy to answer any question you might have in the comments section.
